Item based recommendation, item similarity
Hi there, thanks for the excellent lib. I have used a lot of the great features of the library and it's pretty cool.
However, I need to have item based recommendation ("like similar items"). In general I investigated all methods of base model and specific models, unfortunately couldn't find any method for that.
For example we have recommend_user(user=1, n_rec=7) and it return 7 most relevant items for the user.
What I need is recommend_item(item=1, n_rec=7) or recommend_item(user=1, item=1, n_rec=7) which will return 7 most similar items to the mentioned item. Is there a way to achieve this in scope of the lib.
Regards. Galust Betkhemyan
Yes it is possible to achieve this for models that generate item embeddings such as SVD, BPR, ALS, Item2Vec, Caser etc, but different models have different ways. So maybe you can tell me which model you want to use and I'll see what I can do.
@massquantity Hi, thanks for quick response. Currently I use DeepFM to recommend items to a user. The next problem is to have similar item for a specific item. In item2vec as far as I understood sort_topk_items(item) will return k nearest items in embed_size dimensional space. If it's possible to have the solution for the same model (DeepFM), would be perfect, otherwise, what you would suggest as a model just for item similarity?
It would be difficult for DeepFM to achieve that. Some tricky methods might exist, but performance is not guaranteed. So I would choose item2vec too, since it is designed for item silimarity problem.
You are right about the sort_topk_items function, but there is one thing you should be careful about. There are two kinds of ids in this library, i.e. original id and inner id. Original id will be converted to inner id during training and inner id is just for the sake of convenience.
So the argument item in sort_topk_items is actually inner id, and the returned result is also inner id. To convert between original id and inner id, use data_info.item2id and data_info.id2item, which are just dicts.
hi @massquantity , thanks for the answer. I noticed it. sort_topk_items argumen and return are inner_id-s that should be converted. Just one thing I am not sure is for public functions like recommend_user. I understand that inner_id=False, this means the user is not inner id and it's converted by _check_unknown_user function, what about return item_id-s, is it inner or not if inner_id=False? The same question for DeepFM.
Your observation is correct, and it's a mistake that recommend_user function doesn't convert item_ids. Actually the KnnEmbedding class where sort_topk_items lines in is under development and I plan to implement a group of graph-based algorithms that will generate embeddings. So for now if you want to use recommender_user, you have to convert ids by yourself.
This issue doesn't apply to DeepFM because as in line 388 it uses data_info.id2item to convert ids.
@massquantity yes to convert ids in the implementation is not a huge problem. What I use is
sim_items_inner = self.model.sort_topk_items(self.data_info.item2id.get(item_id, self.model.n_items))
sim_items = [self.data_info.id2item.get(i[0], self.model.n_items) for i in sim_items_inner]
this 2 lines for item similarity. Just a think from sort_topk_items, it includes the item itself.
But what confusing me a bit is
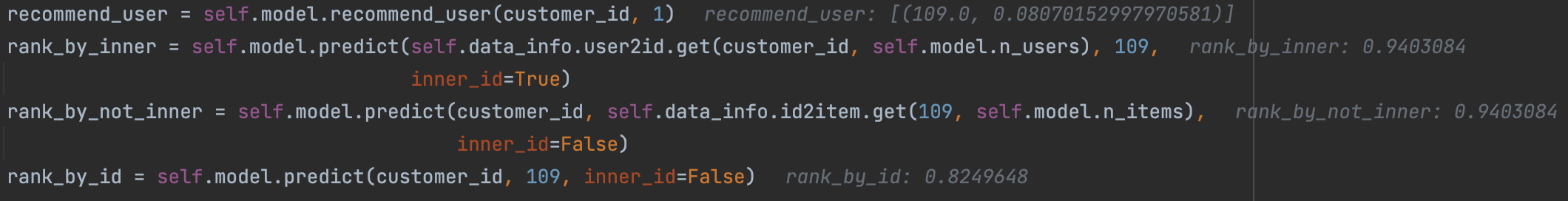
In the image you can see for 109 inner the rank is different, from recommend_user I receive (109, 0.080701) next 2 lines trying to get rank with predict with inner and non inner id-s and I receive 0.9403 The rank_by_id is just a test, like you mentioned it's not inner id what I receive from recommend_user. What is this 0.080701 instead of 0.9403?
The logic in predict and recomender_user is different. In predict, the model computes the similarities between target item 109 and items that the user has interacted, and returns the mean similarities of topk interacted items. In recommend_user, the model computes similarites between every user-interacted item and the whole item set, then finds the most similar items.
The difference is that in predict, the similarities of item 109 and every user-interacted item are guaranteed to contribute to the final result, whereas in recommend_user the most similar items of a user-interacted item may not include item 109, so the score of item 109 comes from less computation.
As I said this algorithm is under development, so I'm not sure what is the most proper way to make prediction and recommendation in this scenario. Maybe I should just provide a public function that returns similar items from a specific item.
@massquantity Thanks for an excellent and useful recommendation library.
I would like to try these algorithms ( Caser , SVD, ALS, BPR, itemCF, NCF ). And i would like to get recommended top 'K' items when given only an "item". No user information will be provided.
Can you please guide me on how to get top 'K' recommended items with above algorithms.
Thanks, Srijith
For algorithms such as Caser , SVD, ALS, BPR, you can use item embeddings generated by the model and perform some similarity metrics such as dot product to get top k items. Different algorithm has different name:
>>> model.fit(...)
>>> item_embed = model.item_vector # Caser
>>> item_embed = model.qi # SVD
>>> item_embed = model.item_embed # ALS, BPR
For ItemCF, similarity matrix generated by the model can be used. However, it is a scipy.sparse.csr_matrix, so one can use this function:
def get_top_k(model, item, k):
sim_matrix = model.sim_matrix
item_slice = slice(sim_matrix.indptr[item], model.sim_matrix.indptr[item+1])
sim_items = sim_matrix.indices[item_slice]
sim_values = sim_matrix.data[item_slice]
top_k_indices = np.argsort(sim_values)[::-1][:k]
return sim_items[top_k_indices]
No such method is available for NCF, or I couldn't think of any:)
Thank you @massquantity. Thanks for putting the top_k method for ItemCF. I will come up with a method for CASER, BPR etc..
In Caser, as per the paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.07426.pdf , in 3.5 Recommendation section, its mentioned as
"to make recommendations for a user u at time step t, we take u’s latent embedding and extract his last L items’ embeddings given by Eqn (2) as the neural network input"
So, ideally it accepts last 'L' items sequence from the user and get the recommendation based on that item sequence. But the default "predict" and "recommend_user" method only accepts "one item"
Is there any thing which i miss here ?
Thanks, Srijith
In _set_last_interacted, _set_latent_factors and user_last_interacted functions, the information of last L items sequence has already been incorporated in the final self.user_vector and self.item_vector, which are used to make predictions and recommendations, so no need to provide items sequence explicitly.
@massquantity Thank you. That explains it.
What i thought was, user would add items in a cart sequentially. So, at the time of recommending an item, Will it be able to send sequence of items to recommend next item, instead of sending only one item for recommendation.
Yeah i was thinking about the same thing when implementing these sequence models, but this would invoke a lot of complexity and MAYBE in the far future i will add a recommend_with_seq method.